EGR valves
What is the EGR valve used for?
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve plays a key role in reducing harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Its main function is to recirculate some of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber of the engine, reducing the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx), one of the main components of smog.
A well-functioning EGR system is therefore essential for maintaining a vehicle’s emission standards and protecting the environment.
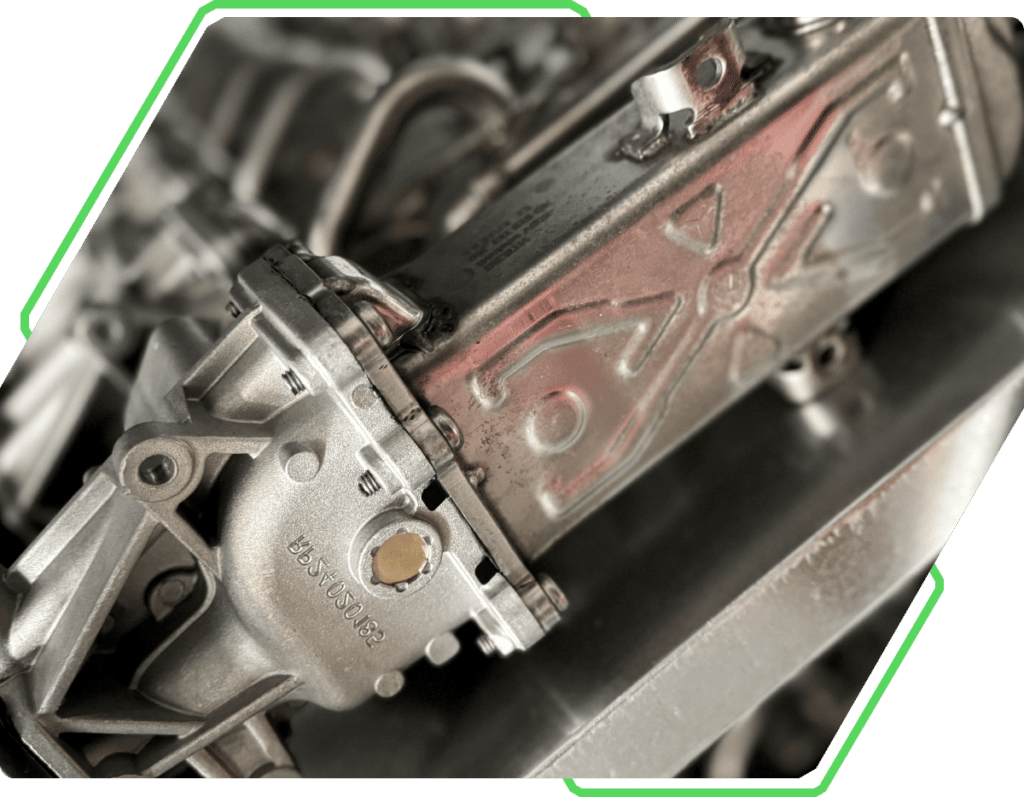
Construction of EGR valve
An EGR valve consists of a housing, a diaphragm or piston, an actuator (electric or pneumatic) and a position sensor. Inside the housing is a channel through which the exhaust gas can flow. Modern EGR valves may also have exhaust gas cooling systems to increase their efficiency.
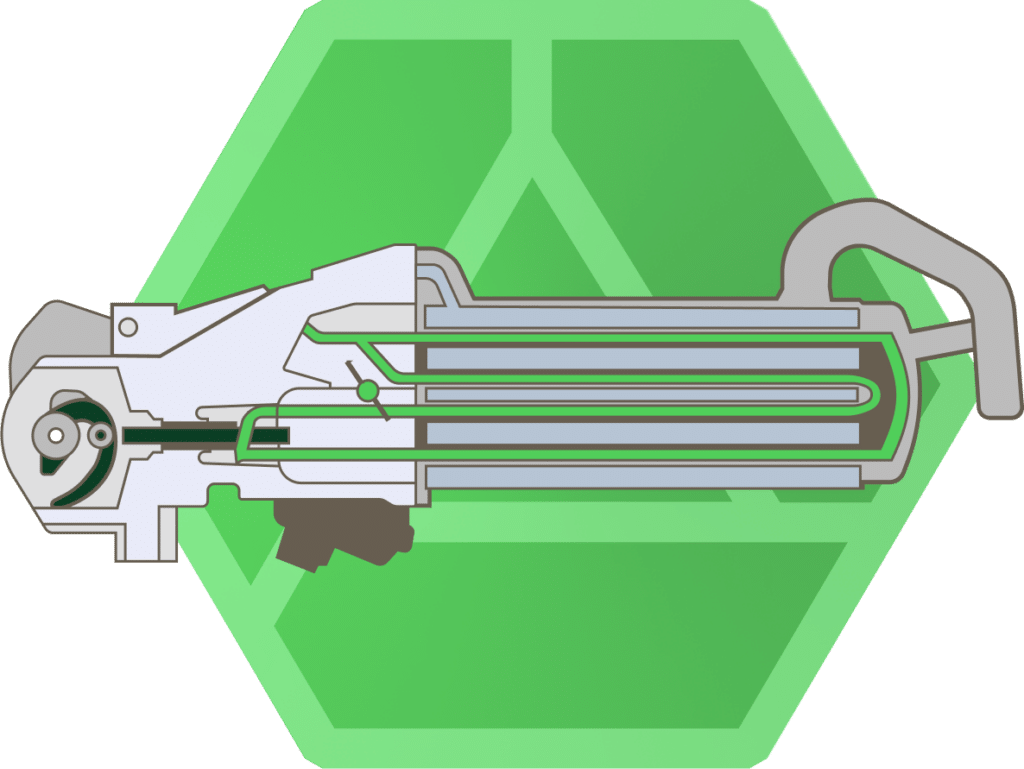
Operating principle of EGR valve
The valve works by mixing the exhaust gases with the intake air, which effectively lowers the combustion temperature in the combustion chamber, reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides. In practice, this means that the EGR valve controls the amount of exhaust back into the cylinder, which not only helps to reduce emissions, but also optimises engine performance, affecting its efficiency and longevity.
The most common EGR valve malfunctions
- Valve blockage due to soot and deposits.
- Damage to the actuator or position sensor.
- Leak in the EGR system causing malfunction and exhaust leak.

How to remanufacture an EGR valve
The most common parts to be remanufactured are the internal components of the valve, such as the piston or diaphragm. If the actuator is damaged, it is usually replaced with a new one. Cleaning the exhaust flow channels of accumulated deposits is a standard remanufacturing step.